Current-voltage Curves
The shape of the current (I) versus voltage (V) of an open channel depends on the permeability of the channel, with its intrinsic voltage dependence, the concentrations on both sides of the channel and the temperature. A simple approximation, that allows an explicit solution of the electrodiffusion equation, assumes a constant field in the channel. This program computes the I-V curve of open pores as a function of the ionic concentrations and temperature. Two cases are available:
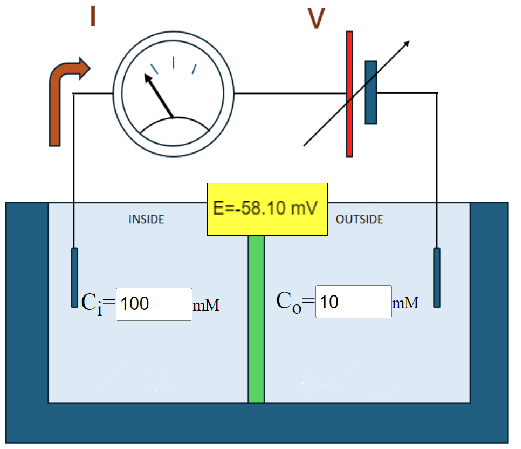
1. One single ionic species. The user may modify the ionic concentrations, the valence of the permeant ion and its polarity (cation or anion) in addition to the temperature. As this is one ion species, the voltage at zero current corresponds to the equilibrium potential, represented by E.
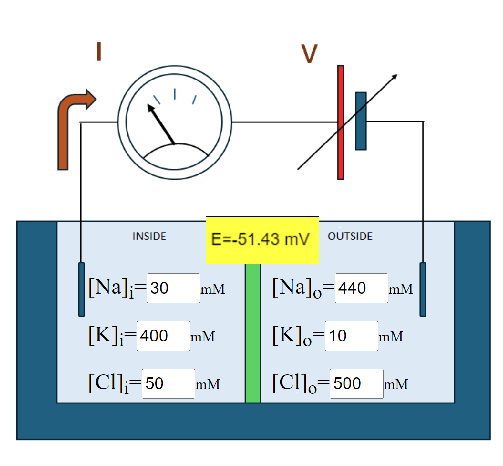
2. Several ionic species. In this case, three different selective pathways: Na+, K+ and Cl- are modeled simultaneously, each channel with its permeabily (PNa, PK and PCl) to compute the resultant I-V curve and the zero current voltage, wich now corresponds to the reversal potential (E). Notice that this situation also corresponds to a single pathway that is permeable to each of the above ionic species.